Usyd大学计算机科学comp5046课程的期末复习
Hello~大家好,今天学姐为留学生分享Usyd大学计算机科学comp5046这门课程辅导,这期的内容主要是分享优秀同学的笔记,学姐整理了非常详细的流程细节可以参考。
课程信息
+ -作业
+ -实验室练习
第一讲
NLP简介
+ -单词表示
++-WordNet
++-一热向量
第二讲
+ -更多单词表示
+ - + -单词包(BoW)
+ - + -术语频率-逆文档频率(TFIDF)
+ -基于预测的单词表示
+ - + - Word2Vec
+ - + -快速文本
+ - + -手套
第三讲
+ -单词嵌入评估
+ -自然语言处理中的深度学习
第四讲
++机器学习和自然语言处理
+ - Seq2Seq学习
+ - + -递归神经网络(RNN)
+ - + -长短期记忆(LSTM)
+ - + -门控循环单元(GRU)
+ - Seq2Seq编码和解码
+ - RNNs
+ -其他
第五讲
+ -聊天机器人
++面向目标的会话代理
++-主动性
++面向聊天的会话代理
++语言基础
++自然语言处理水平
++-文本预处理
第六讲
+ -词性标注
++基线方法
+ -概率方法
+ -深度学习方法
第七讲
+ -依赖结构
++依赖解析算法
+ -评估
第八讲
++语言模型
++-传统语言模型
++神经语言模型
+ -自然语言生成(NLG)
++其他方法
+ -评估
第九讲
+ -信息提取
++命名实体识别(NER)
++-评估
++基于规则的系统
++统计方法
+ - + - Seq2seq代表NER
+ -共同参考分辨率
+ - + -提及配对
+ - + -提到排名
第十讲
+ -关系抽取
++手工构建(基于模式或规则)的方法
++监督方法
++半监督/远程方法
+ -情感分析
第11讲
+ -问答
++基于知识
++基于红外
++-VISual问答
第12讲
+ -机器翻译
++基于规则的机器翻译
++-统计机器翻译
++神经机器翻译
+ -一般来说
++-如何评价机器翻译?
++-机器翻译的总体问题
第十三讲
+ -复习
+ -考试
Course information
Assignments
Assignment 1, week 8 Friday
Assignment 2: week 13 Friday
Using
• Python
• Tensorflow, Keras
• Google Colab
Lab exercises
There are 11. You only need to complete 10 to get the whole 10%.
Google Colab provides a free runtime instance for use.
• https://colab.research.google.com/
• Maximum 24 hour runtime
Lecture 1
Introduction to NLP
NLP is about communcation
• Intention
• Generatation
• Synthesis
Why is NLP different to other fields of AI?
3
• AI is typically centered around numbers and categories
– Things are clearly defined
• Language has ambiguity
– Words have many meanings
Word representation
The aim is to represent language in a way we can feed to a machine. Making
language discrete.
WordNet
• Building a word network (words linked using synoyms)
Problems with solutions like Wordnet
• Nuance of words is lost with synoyms
• Language changes over time
• Requires human effort to maintain, add new words
One-hot vectors
• Represent words as a sparse vector
• One-hot vectors are vectors with a single 1 value, everything else 0 value
Problems with one-hot vectors
• Inefficient
– Vector dimension equals number of words in vocabulary
• No natural idea of word similarity
– All one-hot vectors are orthogonal
• Instead: encode similarity in the vector
– Build a dense vector
Lecture 02
More word representation
Bag of words (BoW)
• All words in a corpus are thrown into a bag
• From this bag, we can derive the vocabulary and a measure of how often
the words appear (occurence)
• It does not care about the order of the original corpus
Problem with bag of words approach
• Meaning is in the order of the words
– “this is interesting” vs “is this interesting?”
4
Term frequency-inverse document frequency (TFIDF)
• Term frequency is the the number of times a words occurs in a given
document
• Inverse document frequency is the number of times a word occurs in a
corpus (many documents)
Prediction-based word representation
Word2Vec
• Considers context
– It looks at the set of words which surround the center word
• Two models
– Continuous bag of words (CBOW)
– Skip-gram
CBOW Model
• Predict the center word from a bag of context words
• Context words are input to the neural network
Skip-gram Model
• Predict the context words from the center word
• Works better with infrequent words
• Centre word is input for a neural network and the output is the context
words
Limitations
• Cannot cover morphological similarities
– e.g. teach, teaching, teacher are treated as completely different words
• Hard to predict rare words
– The NN is example-based. It is underfitting.
• Cannot handle words out-of-vocabulary (OOV)
• If the word is spelled the same, it is considered the same word (homonyms)
FastText
• Word2Vec but with n-grams
• Deals better with rare and OOV words
– because it is likely that part of the new word has been seen before in
the training corpus
• Focus on local context windows, rather than word occurrence
GloVe
• Both Word2Vec and FastText consider context words local to a center
word
5
– This is performed one window at a time
– It does not consider anything beyond the local scope
• GLOVE builds a co-occurence matrix
– Counts how often a word appears in a context
– Performs dimenionality-reduction on the matrix (e.g PCA)
Training data reflects the prediction result.
• Training NN on Google News will produce different machine model to
training NN on Twitter data
Lecture 03
Recap:
• Word2Vec is based on a sliding window of words
– Predicting center word = CBOW
– Predicting context words = Skipgram
• Fasttext can deal with unseen words by applying n-grams
Word embedding evaluation
Intrinsic, extrinsic
• Intrinsic: Evaluate the embedding model on a specific subtask, or intermediate subtask
– For example, if you are building a Question-Answering system, instrinsic evaluation would be evaluating the word-embedding component
individually to assess how well it performs
– Fast to compute
– Unclear if the real task is anything like the subtask task
• Extrinsic: Evaluate the model on a real task
– For example, if you are building a Question-Answering syste, extrinsic evaluation would be evaluating the word-embedding model by
evaluating the entire QA system
– Can take a long time to compute
– Unclear if it interacts with other systems
Deeplearning in NLP
An neuron has
• Function with parameters
• Cost and optimiser functions
Parameters and hyper-parameters
• Parameters
– They are tunable
6
– They are learned from training data
• Hyper-parameters
– Variables controlling how parameters are learned
– e.g. Learning rate, model size/depth
Lecture 04
Machine learning and NLP
NLP methodology
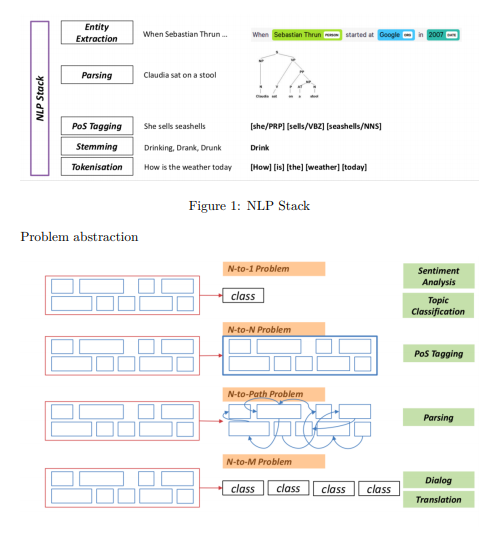
Figure 2: N:M Mapping of problems in NLP
7
Seq2Seq learning
Given a sequence, generate a sequence
Examples
• PoS tagging — words to part of speech
• Speech to text — frames to words
• Movie frame labelling — frames to labels
• Machine translation — words to words
• Sentence completion — words to single word (autocomplete)
Recurrent NN (RNN)
Recurrent (read: re-current. . . last output concatenated with the new input)
• Input is not aware of future inputs
• Vanishing gradient, limited long term memory
– Data input a long time ago may be lost in future noise
Long short-term memory (LSTM)
• Each cell maintains cell state
– Memory cell decide when new information enters, when it is output,
and when it is forgotten (using input, output, and forget gates)
• Computationally intensive because of many gates/calculations
Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
• Similar to LSTM, but does not cell state
– Fewer gates (update and reset gate)
– Faster computations
• GRU is recommended if you have a larger dataset because it is faster to
train
Many of the GIFs in the lecture slides are sourced from here: https://towardsdatascience.com/illustratedguide-to-lstms-and-gru-s-a-step-by-step-explanation-44e9eb85bf21
Seq2Seq encoding and decoding
How to reduce the dimensionality of your data?
• Multiply with a weighted vector (kernel)
• We can generalise by adding more kernels
How do add context data to the input of your NN?
• Merge the input data with the context data, OR
• Output the context to the dimensionality as your expected output and
merge with the new input
考而思comp5046课程专业知识与计算机科学相关学科的在线辅导可以加考而思老师微信进行一对一咨询。
凡来源标注“考而思”均为考而思原创文章,版权均属考而思教育所以,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,否则追究法律责任。

kaoersi03